The behavioral approach emphasizes the scientific study of observable behavioral responses and their environmental determinants. John B. Watson and B. F. Skinner were the first behaviorists. Behaviorism dominated psychological research during the first half of the twentieth century.
The central idea behind behaviorism is that only observable behaviors are researchable, inner thoughts and emotions are private and to subjective.
Using basic principles of learning, behavioral theorists see both normal and ab normal behaviors as responses to various stimuli, responses that have been learned through past experience and that are guided in the present by stimuli in the individual’s environment
normal behaviors as responses to various stimuli, responses that have been learned through past experience and that are guided in the present by stimuli in the individual’s environment
Behavioral genetics researchers are finding increasing evidence that cognitive abilities, personality traits, sexual orientation, and psychological disorders are determined to some extent by genetic factors (hereditary) (Reif & Lesch, 2003; Viding et al., 2005).
Learning is defined as a relatively permanent behavioral change. As we learn we alter the way we perceive our environment.
Classical Conditioning, learning by association, is the process of learning that associates an unconditioned stimulus that already brings about a particular response (i.e. a reflex) with a new (conditioned) stimulus, so that the new stimulus brings about the same response.
B. F. Skinner believed that people’s personalities arise from response tendencies and that consequences shape the responses:
Personality IS a group of responses to the environment –
Radical determinism – All behavior is caused –
Operant Conditioning –
Behavior is changed by its consequences –
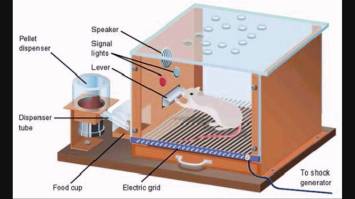
“Skinner box” (operant chamber)
John Watson was the first to study people and how the process of learning affects our behavior and in turn our personalities. Watson’s experiment with Lil Albert concluded that humans could be classically conditioned as were Pavlov’s dogs.
- Founded behaviorismApplied conditioning principles to humans
Rejection of introspection
Tabula rasa approach
John Locke
Lil’ Albert
Albert Bandura said that people learn responses by watching others (observational learning). He believes that thinking and reasoning are important in learning (Social Cognitive Learning).
In response to Behaviorism Bandura believed that behaviorist ignore insights and advances from cognitive and social psychology and that they tend to dehumanize unique human potentials. Bandura disagreed that behavioral theory in itself explains all differences between individuals as a consequence of their reinforcement histories. Behaviorists only view humans as objects to be trained.
Walter Mischel’s research showed that people behave
differently in different situations, “Social Infuences,” Behavior is a function of both the situation and personality: A person’s behavior will vary with the situation, but anchored by personality
Behavioral signature
Recurring situation-behavior relationships
Contributes to the apparent consistency of an individual’s personality
Some situations are so powerful that they override personality effects
A fire in a crowded theater
Implicit Personality Theory
Observers tend to attribute the behaviors of others to personality
Underemphasis on the role of situation
Limited information
People overestimate the consistency of their own behavior
However, people are generally good judges of personality
References:
Bernstein, D.A. & Nash, P.W. (2008). Essentials of psychology (4th ed.) Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company.
Feldman, R. (2013). Essentials of understanding psychology (11th ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Friedman, H.S. & Schustack, M.W. (2012), Personality: classic theories and modern research (5th ed). Boston: Pearson Allyn & Bacon.
McGraw-Hill.McGraw Hill Higher Education (2013), The McGraw Hill Companies, Inc.
Ryckman, R. M. (2013). Theories of personality (10th ed.). Mason, OH: Cengage Learning.

i understand that john watson and Skinner was the first behaviorists.
LikeLike
Read
Behavior is changed by its consequences all the time ?
LikeLike
read an understood
LikeLike
read and understood
LikeLike
Read and understood
LikeLike
Read and somewhat understood
LikeLike
Read and understood
LikeLike
read and agree with the statement As we learn we alter the way we perceive our environment.
LikeLike
I do not fully understand this , have touched on this when receiving my LADC but not in depth.
LikeLiked by 1 person
I read and understood for the most part. I don’t really understand the “Skinner box”
LikeLike
Read and Understood, I agreed with Walter Mischel’s research showed that people behave differently in different situations. We all interact differently with our friends than we do with close loved ones versus how we interact/act or react to things at work or public events.
Operant conditioning kinda confused me because even strong negative or positive reactions to behaviors don’t always mean there is a change in behavior. (For example, a painful splinter in the hand doesn’t mean we stop holding on to railings when going downstairs.)
LikeLike
Read but not sure I understood completely although classical conditioning did make a lot of sense to me
LikeLiked by 1 person
Read and understood !!
LikeLike
Read and somewhat understood. I think Behavioral Psychology is tricky because behavior stems from multiple things, I think it’s tough to put a finger on exactly why people behave the way they do. States that it has a lot to do with learning but maybe some un-learning as well.
LikeLiked by 1 person
read and somewhat understood
LikeLiked by 1 person
read and kinda understood
LikeLiked by 1 person
Read and somewhat understood
LikeLike
read and understood
LikeLike
read and need some more understanding on Classical/Operant Conditioning and Observational Learning
LikeLiked by 1 person
Read and understood most parts
LikeLiked by 1 person
Read and a little confused, hopefully, it will be clearer next class!
LikeLiked by 1 person
read and somewhat understood
LikeLiked by 1 person
read and understood the behavioral psychology
LikeLike
Read and somewhat understood
LikeLiked by 1 person
Read and Understood
LikeLike
Please explain the concepts of operant conditioning
LikeLike
Operant conditioning is behavior that is influenced by it’s consequences. An example is at my job, in order for us to get a positive head count for our Communications Meetings, we state that there will be snacks for the meeting, this spikes up the attendance of the meeting.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Read and Understood
LikeLike
What is it you understand about behavioral psychology??
LikeLike
Sorry, I meant I have read this source and mostly understood. I still need to read the other three sources regarding behavioral psychology to acquire more information to prepare for the next class. Thank you.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Very good!!
LikeLike
read and understood
LikeLike
Read and Understood.
LikeLike
Read & understood
LikeLike
Read and understood!
LikeLike
read and somewhat understood
LikeLike
read and somewhat understood
LikeLike
read and understand
LikeLike
read and a little confused!
LikeLiked by 1 person
Read and understand
LikeLiked by 1 person
Read and a little confused on BF Skinner
LikeLiked by 1 person
Read, and confused
LikeLike
read only understood the last 3 perspectives
LikeLike
read and understand!
LikeLike
All set, read and understood
LikeLiked by 1 person
Read and understood! very interesting!
LikeLiked by 1 person
Read it and got it
LikeLiked by 1 person
Read and understood! I just wanted to understand what response tendencies meant in regards to B.F. Skinner.
LikeLiked by 1 person
We will go over response tendencies and class good job and great call!!
LikeLike
read and understand!!!!!!!
LikeLike