Mood Disorders: Severe Disturbances in Emotion
Emotion-Based Disturbance Strong Enough to Intrude on Everyday Life
Major Depression: Extreme Sadness, Despair, With No Obvious Cause
Characterized by:
- Episodes of deep unhappiness
- Loss of interest in life
Mood disorders – Psychological disorders characterized by usually severe or prolonged disturbances of mood.
- The major forms of mood disorder: 1) depressive disorders and 2) bipolar disorders and related disorders (mood swing disorders).
- There are two major types of depressive disorders that vary in severity: major depressive disorder, the more severe type; and persistent depressive disorder, the milder type.
- Bipolar disorders vary in terms of severity – the more severe disorder is called bipolar disorder, whereas the milder disorder is termed cyclothymic disorder (also called cyclothymia).
Secondary symptoms include:
- Elevated or decreased changes in sleep and appetite
- Loss of interest in sex
- Loss of overall energy
- Difficulties concentrating and making decisions
Major Depression:
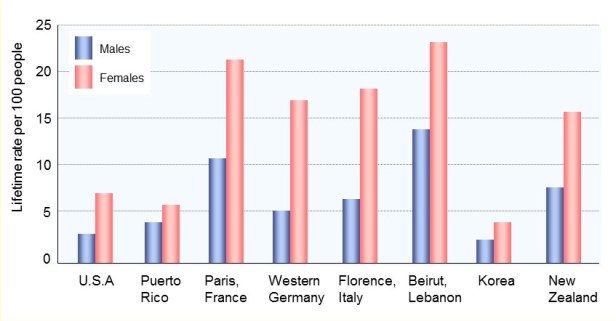
Across different places and cultures women are diagnosed more frequently with depression than men
- Major depressive disorder – A severe mood disorder characterized by major depressive episodes in the absence of mania or hypomania.
- Mania – A state of unusual elation, energy, and activity.
- Hypomania – A relatively mild state of mania.
Major depression impairs people’s ability to meet the ordinary responsibility of everyday life.
- People with major depression may lose interest in most of their usual activities and pursuits, have difficulty concentrating and making decisions, have pressing thoughts of death, and attempt suicide.
- They even show impaired driving skills in driving simulation tests (Bulmash et al., 2006).
Factors that place people at increased risk of developing major depression include:
- Age (initial onset is most common among young adults)
- Socioeconomic status (people lower down the socioeconomic ladder are at greater risk than those who are better off)
Bipolar Disorder: Severe Mood Swings From Depressive to Manic Episodes
- Characterized by:
- An internal struggle with depression (usually the dominant state)
- Alternated with periods of mania, a state of highly excited moods of euphoria and grandeur
Dysthymia: Moderate Depressive Symptoms
- A form of depression that has less dramatic effects on personal and occupational functioning
- Can also last for longer periods than major depression
- People with persistent depressive disorder may have either chronic major depressive disorder or a chronic but milder form of depression called dysthymia.
- Dysthymia derives from Greek roots dys–, meaning “bad” or “hard,” and thymos, meaning “spirit.”
- People with dysthymia feel “down in the dumps” most of the time, often for years, but are not as severely depressed as those with major depressive disorder.
Cyclothymia: Moderate Mood Swings
- A mild form of depression that may include long-term bouts of irritability
- Likened to a milder form of dysthymia
Causes of Mood Disorders:
Psychoanalytic:
- Occurs when an early traumatic loss or rejection creates vulnerability that is not properly resolved
Behavioral:
- Learned via reinforcement
- May be triggered by a loss or some other punishing event
Cognitive:
- A person’s perceptions, thoughts, or self statements cause feelings of worthlessness and inadequacy
Biological:
- Created through genetics and neuro-chemical factors
Family Issues:
- Caused from our surrounding culture, family, friends, and the presence or absence of a strong social support network when dealing with negative factors
References:
Bernstein, D.A. & Nash, P.W. (2008). Essentials of psychology (4th ed.) Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company.
Comer, R.J. (2013). Abnormal Psychology (8th ed). Worth Publishers
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, (DSM-5) American Psychiatric Publishing, 2013
Feldman, R. (2013). Essentials of understanding psychology (11th ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Friedman, H.S. & Schustack, M.W. (2012), Personality: classic theories and modern research (5th ed). Boston: Pearson Allyn & Bacon.
McGraw-Hill.McGraw Hill Higher Education (2013), The McGraw Hill Companies, Inc.
Ryckman, R. M. (2013). Theories of personality (10th ed.). Mason, OH: Cengage Learning.
Sue,Sue, and Sue (2014). Understanding Abnormal Behavior (10th Ed), Cengage Learning
