QUICK REVIEW:
 Motivation: Set of factors that activate, direct, and maintain behavior, usually toward a goal: Specific need of desire, hunger, thirst, or achievement that prompts goal directed behavior
Motivation: Set of factors that activate, direct, and maintain behavior, usually toward a goal: Specific need of desire, hunger, thirst, or achievement that prompts goal directed behavior
Emotion: Subjective feeling including arousal, cognitions, and expressions: feelings such as fear, joy, or surprise that underlies behavior
Theories and Concepts of Motivation:
- Motivation and Behavior
- Theories and Concepts of Emotion
- Critical Thinking about Motivation and Emotion
Biological Theories:
- Instinct
- Drive Reduction
- Arousal
Perspectives on Motivation:
– Instinct
- Inborn, unlearned, goal directed behavior that is characteristic of an entire species
- Human behavior is not easily explained by instincts because:
–Important Human behavior is learned
–Human behavior is rarely inflexible
Drive Reduction Theory 
- Internal tensions “push” toward satisfying basic needs
- State of tension caused by bodily needs
- Theory is that motivated behavior is an attempt to reduce a drive and return the body to homeostasis
- Primary Drive: unlearned drive such as hunger based on a physiological state
- Secondary Drive: learned drive such as ambition
Arousal Theory
- Motivated to seek an optimal level of arousal for a given moment
- Yerkes-Dodson Law: there is an optimal level or arousal for best performance on any task
- The more complex the task, the lower the level of arousal that can be tolerated without interfering with performance
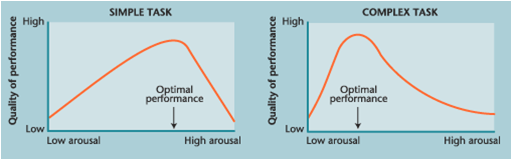
Optimal Level of Arousal: People seek an optimal level of arousal that maximizes their performance
Psychosocial Theories:
– Incentives
Motivation that results from the “pull” of external environmental stimuli: External stimuli that prompts goal directed behavior, often, we are unaware of the incentive, for example: Aroma of food may cause us to eat even when we are not hungry, advertisements that lead us to buy a product we do not necessarily need
– Cognitive
- Motivation affected by attributions and expectations:
- Intrinsic motivation: motivation for a behavior is the behavior itself, example children enjoy playing on the swing set
- Extrinsic motivation: Behavior is performed in order to obtain a reward or to avoid punishment: cash incentives at work
Bio-Psychosocial Theories:
- Interaction of biological, psychological, and social needs; lower motives (physiological andsafety) must be met before higher needs (belonging, self-esteem)
Motivation and Behavior – Hunger and Thirst
- Psychological factors: visual cues and cultural conditioning
- Cultural and Environmental factors: Repsonses to food are governed by learning and social conditioning, culture influences what we choose to eat
- Obesity: Results from numerous biological and psychosocial factors
- Anorexia nervosa/Bulimia Nervosa: results from fear of becoming obese resulting from numerous biological and psychosocial factors
Motivation and Behavior – Achievement
- High need for achievement
- Prefers moderately difficult tasks
- Prefers clear goals with competent feedback
- Competitive
- Prefers responsibility
- Persistent
- More Accomplished
Emotion:
Three Components of Emotion
- Physiological: Arousal comes from the brain, particularly the limbic and autonomic nervous system
- Cognitive: Thoughts, values, and expectations
- Behavioral: Expressions, gestures, and body position
Emotion:
- Fear
- Happiness
- Surprise
- Sadness
- Disgust
- Anger
- Anticipation
- Joy
- Acceptance
Intrinsic Versus Extrinsic Motivation:

Intrinsic rewards come from within – no monetary value.
Extrinsic rewards may lower interest and motivation.
Emotional Intelligence (EI): Is the ability to know and manage one’s emotions, empathize, and maintain satisfying relationships.
References:
Bernstein, D.A. & Nash, P.W. (2008). Essentials of psychology (4th ed.) Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company.
Feldman, R. (2013). Essentials of understanding psychology (11th ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Friedman, H.S. & Schustack, M.W. (2012), Personality: classic theories and modern research (5th ed). Boston: Pearson Allyn & Bacon.
McGraw-Hill.McGraw Hill Higher Education (2013), The McGraw Hill Companies, Inc.
Ryckman, R. M. (2013). Theories of personality (10th ed.). Mason, OH: Cengage Learning.

Read the video helped a little better with understanding the concept of Motivation and Emotion
LikeLike
Read and understood.
LikeLike
Professor I did read this as well I forgot to post “read” I will talk to you after class
LikeLike
Read and understood!!
LikeLike
read it and understood
LikeLike
read and understand
LikeLike
read/ watched didn’t quite understand Maslow’s Theory
LikeLiked by 1 person
Read
LikeLike
Read and understood slightly more than quick review for Memory!
LikeLike
read and understand most parts
LikeLike
read and confused
LikeLike
read and kind of understood
LikeLike
read and mostly understood
LikeLike
read and kind of understood
LikeLike
Read and a little surprised , I always thought motivation was connected to our emotions so I’d like to more in detail about this topic to better understand the differences..
LikeLike
read, and a little confused
LikeLiked by 1 person
read and understand
LikeLike
read, interested subject would love to learn more about
LikeLike