QUICK REVIEW:
Defining Development
The science of human development…Seeks to understand how and why people — all kinds of people, everywhere, of every age — change over time.
Life Stages:
- Begins at birth and ends at death
- During the entire lifespan, individuals have needs that must be met
- Infancy: Birth to 1 year
- Early Childhood: 1 – 6 years
- Late Childhood: 6 – 12 years
- Adolescence: 12 – 20 years
- Early Adulthood: 20 – 40 years
- Middle Adulthood: 40 – 65 years
- Late Adulthood: 65 years and up
Growth and Development Types:
- Physical: Body Growth
- Mental: Mind Development
- Emotional: Feelings

- Social: Interactions and relationships
All four growth types occur in each stage of development
All Stages of Development
- Physical Development
- Mental Development
- Emotional Development
- Social Development
- Needs
- (During Infancy, dramatic and rapid changes, infants are dependent for all needs)
The Life-Span Perspective:
Development is multidirectional
- Over time, human characteristics change in every direction
- Several major theorists describe stages of development: Freud, Erickson, Piaget
- Others view development as a continuous process
Socioeconomic Context – Socioeconomic Status (SES)
A person’s position in society as determined by income, wealth, occupation, education, and place of residence.
Development Is Multicultural
- Culture – patterns of behavior that are passed from one generation to the next.
- Vygotsky described the interaction between culture and education.
- Ethnic group – People whose ancestors were born in the same region and who often share a language, culture, and religion
Development Is Multidisciplinary
- Genetics and neuroscience are two of the newer disciplines in lifespan research.
- Every trait—psychological as well as physical—is influenced by genes.
Theories of Human Development:
A developmental theory is a systematic statement of principles and generalizations that provides a framework for understanding how and why people change as they grow older.
- A theory of human development that holds that irrational, unconscious drives and motives, often originating in childhood, underlie human behavior.
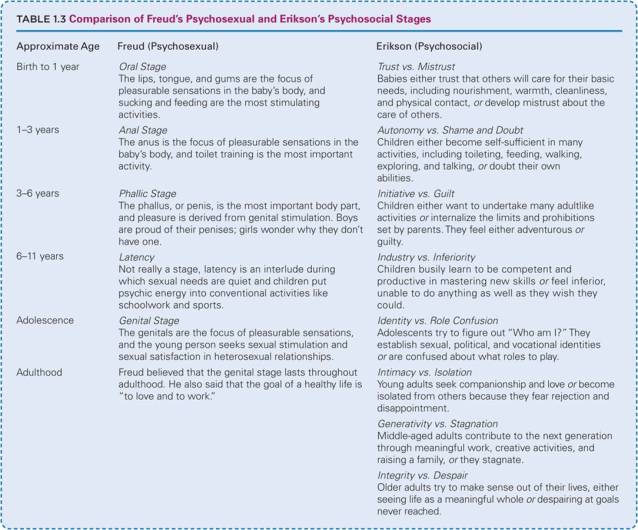
- Psychoanalytic theory originated with Sigmund Freud (1856– 1939)
Erickson’s Stages
- Erik Erikson (1902–1994)
- Described eight developmental stages, each characterized by a challenging developmental crisis.
- His first five stages build on Freud’s theory; but, he also described three adult stages.
- A theory of human development that studies observable behavior. Behaviorism is also called learning theory, because it describes the laws and processes by which behavior is learned.
- Conditioning– According to behaviorism, the processes by which responses become linked to particular stimuli and learning takes place.
Classical Conditioning – Ivan Pavlov (1849-1936)
- (also called respondent conditioning), a process in which a person or animal learns to associate a neutral stimulus with a meaningful stimulus, gradually reacting to the neutral stimulus with the same response as to the meaningful one.
Operant Conditioning – B.F. Skinner (1904–1990)
- (also called instrumental conditioning) a learning process in which a particular action is followed either by something desired (which makes the person or animal more likely to repeat the action) or by something unwanted (which makes the action less likely to be repeated).

Social Learning Theory – Albert Bandura
- An extension of behaviorism that emphasizes the influence that other people have over a person’s behavior.
- Modeling– people learn by observing other people and then copying them.
- Self-efficacy– (how effective people think they are when it comes to changing themselves or altering their social context.
Cognitive Theory
- Thoughts and expectations profoundly affect action.
- Focuses on changes in how people think over time.
- Jean Piaget (1896–1980)

Death and Dying:
- Death is the final stage of growth
- Experienced by everyone and no one escapes
- Young people tend to ignore death
- Elderly begin to think about death
Terminal Illness
- Disease that cannot be cured and will result in death
- People react in different ways
- Some believe death as a final peace
Stages of Death and Dying:
- Anger, can no longer deny death
- Bargaining – accepts death but wants more time
- Depression, realizes death will be soon
- Acceptance, understands and accepts death
- Dignity and Respect in Death
- Death is a part of life
References:
Bernstein, D.A. & Nash, P.W. (2008). Essentials of psychology (4th ed.) Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company.
Feldman, R. (2013). Essentials of understanding psychology (11th ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Friedman, H.S. & Schustack, M.W. (2012), Personality: classic theories and modern research (5th ed). Boston: Pearson Allyn & Bacon.
McGraw-Hill.McGraw Hill Higher Education (2013), The McGraw Hill Companies, Inc.
Ryckman, R. M. (2013). Theories of personality (10th ed.). Mason, OH: Cengage Learning.

Read and understood
LikeLike
Read and understood
LikeLike
Read and understood
LikeLike
read, watched and understood!
LikeLike
So i know i watched this back when this class first started but understand it much better now .
LikeLike
Read and mostly understood
LikeLike
Read and I see the difference stages that human being go through from being born until death. The progression of life.
LikeLike
read and got most of it.
LikeLike
read and understood
LikeLike
Read and mostly understood.
LikeLike
Read and understand some of it
LikeLike
Read and understand the part of Freud theory
LikeLike
Read and understand the basic information. As an adolescent, I see the difference between me right now and when I was a child.
LikeLike
Read and somewhat understood I need to go over the charts again.
LikeLike
Read and understand most of it.
LikeLike
Read and Understood because I am currently taking a child growth and development class and we learned similar information.
LikeLike
Read. I need to go over the charts a bit more to get it to sink in.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Read and only understood part of it.
LikeLike
read and somewhat understood, need more clarification on which theorist goes with which idea and some terms
LikeLike
Read the charts
LikeLike
read and got it!
thank you
LikeLiked by 1 person
Keep up the good work!!
LikeLike
Read this and going over each again
LikeLike
Nice
LikeLike
Read and had difficulties understanding some parts but was able to connect topics to what we discussed in class
LikeLike
i read the beginning and understood it however towards the middle i began to struggle with the different things such as how development Is multidisciplinary
LikeLike
Read it and not going to lie completely lost
LikeLike
read and understood a little
LikeLike
Read and somewhat understood !
LikeLike
I read and understood tis
LikeLike
read and understood most of it
LikeLiked by 1 person
read and understood a little
LikeLike
Read and Understood.
LikeLike
Read and understood
LikeLike
read and somewhat understood
LikeLike
Also reading over some of Freud’s points on cognitive thinking like WTF was he thinking?
LikeLike
Read and understood for the most part, but admit that there were parts of the reading that I didn’t understand.
LikeLike
Read, understood some stages but will need clarification later.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Read/ Watched interesting topic.. didn’t understand
LikeLike
read and definitely like Erikson’s perspective over Freud’s
LikeLiked by 1 person
YES
LikeLike
read and understand most parts
LikeLike
Read & I think I understand for the most part
LikeLike
Read
LikeLiked by 2 people
read and understood a bit but would like to learn more about it.
LikeLiked by 2 people
Read, all I understood is life start with birth and end with death but the rest huge blank
LikeLiked by 2 people
read and understand a little
LikeLiked by 2 people
read and understood a little bit because we learned about these people in class but other wise it was still confusing
LikeLiked by 2 people
read and understood a bit but interesting topic!
LikeLiked by 2 people
Read and tried my best to understand.
LikeLiked by 1 person